



Next: Lab-3 Field Procedure
Up: Lab-3 Activities
Previous: Using the Spectrophotometer
Using the YSI-85
The D.O. meter
will be used to measure dissolved oxygen (DO), electrical
conductivity, and salinity. The device measures six different water
parameters, and is intended for use in moving water. The ``MODE''
button on the meter switches between the following in the order given
below. Press the ``MODE'' button and wait for a few seconds for the
mode to move to the next entry.
Note that D.O. is measured by the
rate of consumption of oxygen at the tip of the probe, so it requires
continual movement of water past the tip (an up-and-down motion seems
to work best, keep the probe tip submerged). Stable readings will not be
possible while the temperature of the sample is changing.
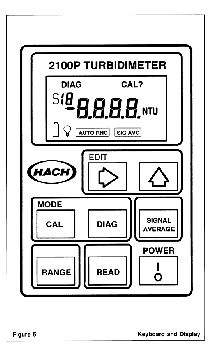
Figure 4.10:
Dissolved oxygen-electrical conductivity-temperature meter (see
manufacturer). Black probe is inserted
into stream (or sample container) for measurement.
|
|
 On/Off
On/Off
- Press the ON/OFF button to turn on the meter. The
instrument will
activate all segments of the display for a few seconds, which will be
followed by a self-test procedure and will last for several more seconds.
The Model 85 will display the cell constant of the conductivity probe
when the self-test is complete (with ``CEL'' shown at the bottom
of the LCD display). Then it will switch to D.O. % mode.
 Temperature (
Temperature (
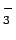 )
)
- always displayed as the last line in the
readout
 Dissolved Oxygen %
Dissolved Oxygen %
- a measurement of oxygen in percent of
saturation. If you are measuring D.O. in a bottled sample,
stir with the probe so that water moves past it at a
rate of around 1
 . Wait until changes in reading
are less than 1% over 15 seconds to record your reading.
. Wait until changes in reading
are less than 1% over 15 seconds to record your reading.
 Dissolved Oxygen
Dissolved Oxygen

- a measurement of oxygen in
 (same as parts-per-million)
(same as parts-per-million)
 Conductivity
Conductivity
- a measurement of the conductive material in the liquid
sample without regard to temperature (units are micro-siemens or
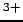 ). Be sure the two holes near the cable on the sensor are
submerged; these make the conductivity measurement
). Be sure the two holes near the cable on the sensor are
submerged; these make the conductivity measurement
 Specific Conductance
Specific Conductance
- also known as compensated conductivity which
automatically adjusts the reading to a calculated value which would have
been read if the sample had been at 25
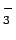 (units are micro-siemens or
(units are micro-siemens or
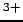 )
)
 Salinity
Salinity
- a calculation done by the instrument electronics,
based upon the conductivity and temperature readings (units are
parts per thousand, or ppt)




Next: Lab-3 Field Procedure
Up: Lab-3 Activities
Previous: Using the Spectrophotometer
GEOS 3110 Professor's Notes, Summer 2003
Dr. T. Brikowski, UTD

